Smooth step function
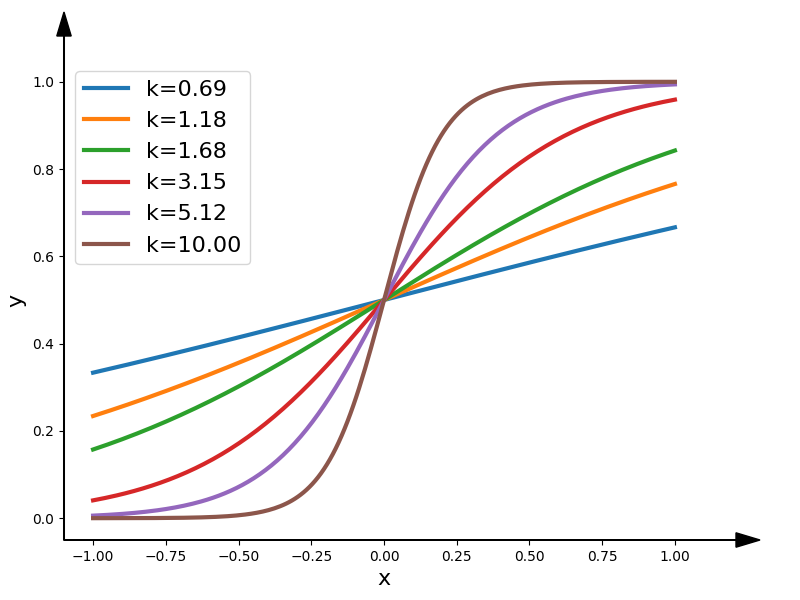
One common example of a smooth step function is the sigmoid function. The sigmoid function is an S-shaped curve and is often used in various fields, including machine learning, neural networks, and image processing. The general form of the sigmoid function is:
$$f(x) = \cfrac{1}{\left(1 + e^{-kx}\right)}$$where $f(x)$ is the output value of the function, $x$ is the input value, $k$ is a constant that controls the slope of the curve.
Higher values of $k$ make the transition steeper, while lower values make it more gradual. $e$ is the base of the natural logarithm, approximately equal to 2.71828. The smoothness of the transition in the sigmoid function makes it useful in situations where you want gradual changes between two states or values. For example, in neural networks, sigmoid functions are often used as activation functions to introduce non-linearity and control the output range of the neurons.
Other smooth step functions can exist, depending on specific applications and requirements. For instance, the "error function" (also known as the "Gaussian error function") is another type of smooth step function used in probability theory, statistics, and solving partial differential equations.